ArduPilot源码阅读——底层油门转向篇
低通滤波器
在AC_AttitudeControl_Sub中写到了一个使用低通滤波器,来防止突然变化的高度信息,使控制器缓慢达到目标值
_althold_lean_angle_max = _althold_lean_angle_max + (_dt/(_dt+_angle_limit_tc))*(althold_lean_angle_max-_althold_lean_angle_max);简化版本为:
y(n+1) = y(n) + dt / (dt + Tc) * (x(n) - y(n))简单的一节低通滤波,Tc代表时间常数,dt采样时间;它是通过拉普拉斯反变换后,在经过后向差分离散得来的。
具体一阶低通滤波器实现请参考 LowPassFilter.h/.cpp
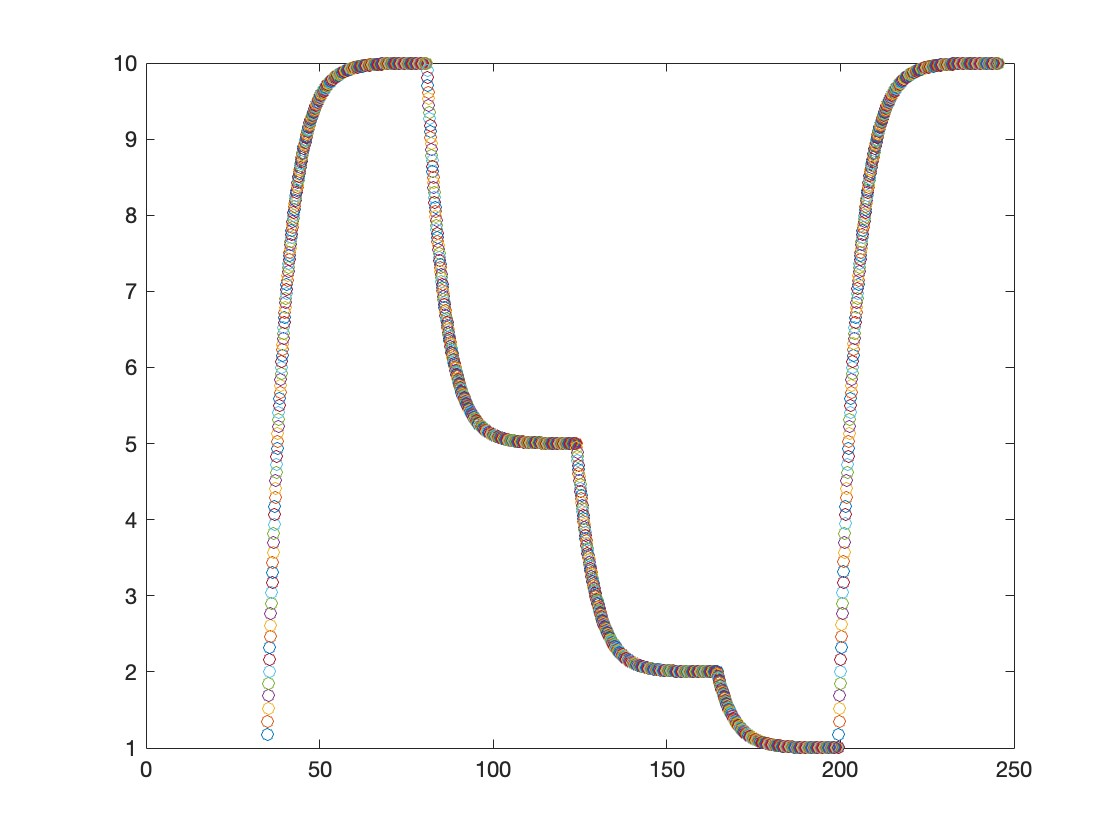
Matlab演示
分别给出几个输入值,可以从图中看出输出缓慢靠近输入的值;

转向缩放(用于油门转弯模型)
输出油门量throttle和转弯量steering,其函数原型为
void AP_MotorsUGV::output_regular(bool armed, float ground_speed, float steering, float throttle)输入分析:
armed: 电机是否在控
ground_speed: 当前地速
steering: 输入转弯量(横向)
throttle: 输入油门量(纵向)
源码分析:
void AP_MotorsUGV::output_regular(bool armed, float ground_speed, float steering, float throttle){
if (armed) { //电机是否在控
if (_scale_steering) { //按速度或者角度来缩放转向
if (have_vectored_thrust()) { //向量推进器,适用对象一般为螺旋桨可变向的船
....
}
....
else{ //按地速来控制转向缩放
....
}
}
else{ //不启用转向缩放
....
}
output_throttle(SRV_Channel::k_throttle, throttle); //输出油门量为pwn(多为无刷电机)
}
else { //电机不在控
if (_disarm_disable_pwm) { //限制电机输出
SRV_Channels::set_output_limit(SRV_Channel::k_throttle, SRV_Channel::Limit::ZERO_PWM);
} else {
SRV_Channels::set_output_limit(SRV_Channel::k_throttle, SRV_Channel::Limit::TRIM);
}
}
set_limits_from_input(armed, steering, throttle); //转弯量,油门量是否到极限,是,则设置limit通知其他进程
steering = constrain_float(steering, -4500.0f, 4500.0f);
SRV_Channels::set_output_scaled(SRV_Channel::k_steering, steering); //输出转弯量为pwm(多为舵机)
}if (have_vectored_thrust()) { //向量推进器,适用对象一般为螺旋桨可变向的船
// normalise desired steering and throttle to ease calculations
// 这里所传入的steering与throttle为横向与纵向量!
float steering_norm = steering / 4500.0f; //从归一化可以看出 允许输入的转弯变化范围-+45
const float throttle_norm = throttle * 0.01f; //允许输入的油门范围为百分比表示
/* ************************************************************************* */
// steering can never be more than throttle * tan(_vector_angle_max)
/*
* 这里是保证 steering/throttle 不超过tan(vector_angle_max_rad)
* 确保后面计算steering_angle的时候,steering_angle不会超过 vector_angle_max
*/
const float vector_angle_max_rad = radians(constrain_float(_vector_angle_max, 0.0f, 90.0f));
const float steering_norm_lim = fabsf(throttle_norm * tanf(vector_angle_max_rad));
if (fabsf(steering_norm) > steering_norm_lim) {
if (is_positive(steering_norm)) {
steering_norm = steering_norm_lim;
}
if (is_negative(steering_norm)) {
steering_norm = -steering_norm_lim;
}
limit.steer_right = true;
limit.steer_left = true;
}
/* ************************************************************************* */
if (!is_zero(throttle_norm)) {
// 计算实际steering_angle转弯角度
float steering_angle_rad = atanf(steering_norm / throttle_norm);
// limit steering angle to vector_angle_max
if (fabsf(steering_angle_rad) > vector_angle_max_rad) {
steering_angle_rad = constrain_float(steering_angle_rad, -vector_angle_max_rad,\
vector_angle_max_rad);
limit.steer_right = true;
limit.steer_left = true;
}
// 将steering_angle按照最大转角映射为-4500~4500
steering = steering_angle_rad / vector_angle_max_rad * 4500.0f;
// throttle(纵向)根据转角大小转化真实的throttle(沿矢量方向)
const float throttle_scaler_inv = cosf(steering_angle_rad);
if (!is_zero(throttle_scaler_inv)) {
throttle /= throttle_scaler_inv;
}
}
} else { //正常的后轮驱动,前轮转向模型
// scale steering down as speed increase above MOT_SPD_SCA_BASE (1 m/s default)
if (is_positive(_speed_scale_base) && (fabsf(ground_speed) > _speed_scale_base)) {
steering *= (_speed_scale_base / fabsf(ground_speed));
} else {
// regular steering rover at low speed so set limits to stop I-term build-up in controllers
if (!have_skid_steering()) {
limit.steer_left = true;
imit.steer_right = true;
}
}
// reverse steering direction when backing up
if (is_negative(ground_speed)) {
steering *= -1.0f;
}
} 滑动转向(用于履带车等差速模型)
输出油门量throttle和转弯量steering,函数原型:
void AP_MotorsUGV::output_skid_steering(bool armed, float steering, float throttle, float dt)输入参数:
armed: 电机是否在控
steering: 输入转弯量(横向)
throttle: 输入油门量(纵向)
源码分析:
{
//判断是否滑动转弯模型
if (!have_skid_steering()) {
return;
}
// 清除转向,油门限制
set_limits_from_input(armed, steering, throttle);
// 限制转向
steering = constrain_float(steering, -4500.0f, 4500.0f);
// 处理不在控电机情况
if (!armed) {
if (_disarm_disable_pwm) {
SRV_Channels::set_output_limit(SRV_Channel::k_throttleLeft,RV_Channel::Limit::ZERO_PWM);
SRV_Channels::set_output_limit(SRV_Channel::k_throttleRight,RV_Channel::Limit::ZERO_PWM);
} else {
SRV_Channels::set_output_limit(SRV_Channel::k_throttleLeft, SRV_Channel::Limit::TRIM);
SRV_Channels::set_output_limit(SRV_Channel::k_throttleRight, SRV_Channel::Limit::TRIM);
}
return;
}
/* ************************************************************************* */
/* ************************** 滑动转向混合器 ******************************** */
float steering_scaled = steering / 4500.0f; // steering scaled -1 to +1
float throttle_scaled = throttle * 0.01f; // throttle scaled -1 to +1
// 界定推力不对称程度thrust_asymmetry
//不对称因子 —— 车速前进与后退是否一致的速度
const float thrust_asymmetry = MAX(_thrust_asymmetry, 1.0);
//反向油门能力最大值(这里的限值量是用作量化计算的,衡量理论上最大倒退能力,相对于正向)
const float lower_throttle_limit = -1.0 / thrust_asymmetry;
/**
* 根据前进能力与后退能力的中值 来衡量其最佳转向油门
* 比如说 当反向后退能力最大为-0.5时(此时不对称因子为2),最佳转向油门为0.25
* 即 在油门值为0.25的情况下,剩余的双向油门空间最大
* 正向:1~0.25 区间为0.75
* 反向:-0.5~0.25 区间为-0.75
*/
// Maximum steering is half way between upper and lower limits
const float best_steering_throttle = (1.0 + lower_throttle_limit) * 0.5;
float steering_range;
if (throttle_scaled < best_steering_throttle) {
/**
* 当油门低于最佳转向油门
* 1. 控制油门量为正(前进),转向区间受限于反向后退能力,但不固定(向下可用空间)
* 2. 控制油门量为负(后退),转向区间受限于反向后退能力,且固定(向下可用空间)
* “固定”的因素为”倒车“是一种特殊情况,一般情况下利用正向来控制,而不是倒退
*
* 为什么取决于反向能力?
* 是因为油门量在后续油门转向混合中不会增加,即不会超过他现在的值,
* 最大转弯能力(throttle_range)取决于lower_throttle_limit
*/
// steering range is reduced as throttle will never be increased by mixer
steering_range = MAX(throttle_scaled,0.0) - lower_throttle_limit;
} else {
/**
* 当油门高于最佳转向油门
* 转向区间为最大转弯能力(1-best_steering_throttle)
* 为什么是最大转弯能力,是因为油门量总是可以降低到最佳转弯油门
*/
// full range available, throttle can always be lowered down to best_steering_throttle
steering_range = 1 - best_steering_throttle;
}
// 约束转向
if (steering_scaled > steering_range) {
limit.steer_right = true;
steering_scaled = steering_range;
} else if (steering_scaled < -steering_range) {
limit.steer_left = true;
steering_scaled = -steering_range;
}
// 约束油门
if (throttle_scaled > 1.0) {
limit.throttle_upper = true;
throttle_scaled = 1.0;
} else if (throttle_scaled < lower_throttle_limit) {
limit.throttle_lower = true;
throttle_scaled = lower_throttle_limit;
}
// 现在thrott与steering分别都满足要求, 以下检查他们组合在一起后是否也满足要求
const float max_output = throttle_scaled + fabsf(steering_scaled);
const float min_output = throttle_scaled - fabsf(steering_scaled);
// 计算饱和度,并据此按比例缩放throttle和steering
const float max_output = throttle_scaled + fabsf(steering_scaled);
const float min_output = throttle_scaled - fabsf(steering_scaled);
// 计算饱和度,据此按比例缩放throttle和steering
const float saturation_value = MAX(max_output, min_output / lower_throttle_limit);
if (saturation_value > 1.0f) {
// 备份,方便后面判断是否操作了throttle和steering
const float steering_scaled_orig = steering_scaled;
const float throttle_scaled_orig = throttle_scaled;
// str_thr_mix用于界定输出饱和后,throttle和steering修改优先比例
/**
* str_thr_mix = 0.5 throttle和steering按相同比例缩放
* str_thr_mix > 0.5 steering将具有更大的缩放优先度(str_thr_mix-0.5)
* str_thr_mix < 0.5 throttle将具有更大的缩放优先度(str_thr_mix-0.5)
* P.S. 具有优先度者,将缩小更少的值,而另一者将缩小更大的值
*/
const float str_thr_mix = constrain_float(_steering_throttle_mix, 0.0f, 1.0f);
const float fair_scaler = 1.0f / saturation_value;
if (str_thr_mix >= 0.5f) {
// prioritise steering over throttle
steering_scaled *= linear_interpolate(fair_scaler, 1.0f, str_thr_mix, 0.5f, 1.0f);
if (throttle_scaled >= best_steering_throttle) {
// throttle大于最佳值时,输出上限决定其大小
throttle_scaled = 1.0 - fabsf(steering_scaled);
} else {
// throttle小于最佳转弯值时,输出下限决定其大小,这种情况用于throttle<0的情况
/**
* throttle小于最佳转弯值时,输出又饱和
* 若throttle>0,不可能发生throttle+steering>1的情况
* 其情况只有throttle<0时
*/
throttle_scaled = fabsf(steering_scaled) + lower_throttle_limit;
}
} else {
// 同上理
throttle_scaled *= linear_interpolate(fair_scaler, 1.0f, 0.5f - str_thr_mix, 0.0f, 0.5f);
const float steering_sign = is_positive(steering_scaled) ? 1.0 : -1.0;
if (throttle_scaled >= best_steering_throttle) {
// constrained by upper limit
steering_scaled = (1.0 - throttle_scaled) * steering_sign;
} else {
// constrained by lower limit
steering_scaled = (throttle_scaled - lower_throttle_limit) * steering_sign;
}
}
// 判断是否发生了缩放,若发生缩放,说明已经到达极限
if (fabsf(steering_scaled) < fabsf(steering_scaled_orig)) {
limit.steer_left |= is_negative(steering_scaled_orig);
limit.steer_right |= is_positive(steering_scaled_orig);
}
if (fabsf(throttle_scaled) < fabsf(throttle_scaled_orig)) {
limit.throttle_lower |= is_negative(throttle_scaled_orig);
limit.throttle_upper |= is_positive(throttle_scaled_orig);
}
}
// 合并
float motor_left = throttle_scaled + steering_scaled;
float motor_right = throttle_scaled - steering_scaled;
// 反转不对称修正
if (is_negative(motor_right)) {
motor_right *= thrust_asymmetry;
}
if (is_negative(motor_left)) {
motor_left *= thrust_asymmetry;
}
// 转化为pwm
output_throttle(SRV_Channel::k_throttleLeft, 100.0f * motor_left, dt);
output_throttle(SRV_Channel::k_throttleRight, 100.0f * motor_right, dt);
}油门缩放
参数分析:
throttle:输入油门量大小(范围-100~100)
_throttle_min:油门死区
_thrust_curve_expo:低转低扭补偿(拉高低速油门时的转速,使其油门与推力关系更线性)
源码分析:
float AP_MotorsUGV::get_scaled_throttle(float throttle) const
{
// 油门为0则返回
if (is_zero(throttle)) {
return throttle;
}
// 补偿油门死区 把 0-100 映射到 throttle_min~100
if (_throttle_min > 0) {
if (is_negative(throttle)) {
throttle = -_throttle_min + (throttle * ((100.0f - _throttle_min) * 0.01f));
} else {
throttle = _throttle_min + (throttle * ((100.0f - _throttle_min) * 0.01f));
}
}
// 判断是否进行油门低位曲线补偿
if (is_zero(_thrust_curve_expo) || (_thrust_curve_expo > 1.0f) || (_thrust_curve_expo < -1.0f)) {
return throttle;
}
// calculate scaler
const float sign = (throttle < 0.0f) ? -1.0f : 1.0f;
const float throttle_pct = constrain_float(throttle, -100.0f, 100.0f) * 0.01f;
/**
* 补偿模型为过(0,0) (1,1)的开口向右的抛物线,参数为_thrust_curve_expo
* 曲线图像如下所示
*/
return 100.0f * sign * ((_thrust_curve_expo - 1.0f) + safe_sqrt((1.0f - _thrust_curve_expo) * (1.0f - _thrust_curve_expo) + 4.0f * _thrust_curve_expo * fabsf(throttle_pct))) / (2.0f * _thrust_curve_expo);
}
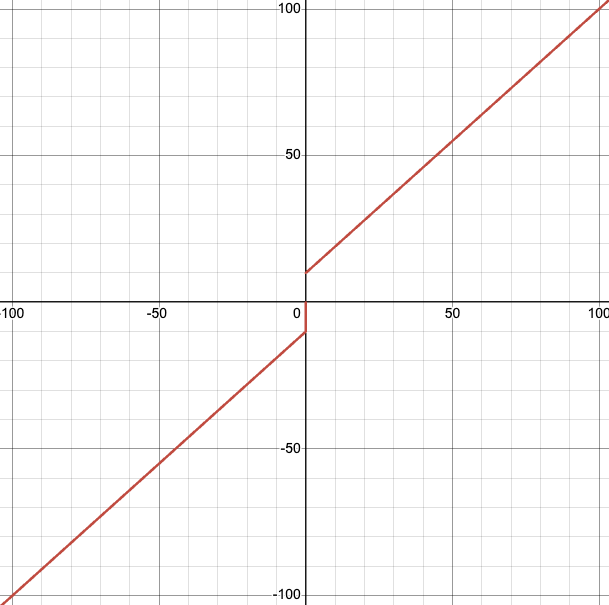
对于油门死区缩放:
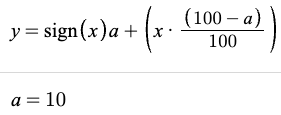
对于油门推力补偿:
红色线段为  绿色线段为
绿色线段为
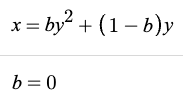
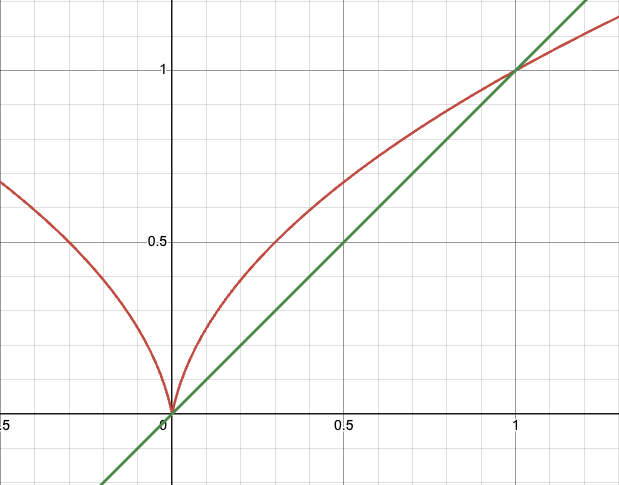
可见在低油门下,可以通过调整参数,来提高低油门转速,进而线形推力。
待研究代码
ModeCircle
void ModeCircle::update()
{
// get current position
Vector2f curr_pos;
const bool position_ok = AP::ahrs().get_relative_position_NE_origin(curr_pos);
// if no position estimate stop vehicle
if (!position_ok) {
stop_vehicle();
return;
}
// Update distance to destination and distance to edge
const Vector2f center_to_veh = curr_pos - config.center_pos;
_distance_to_destination = (target.pos.tofloat() - curr_pos).length();
dist_to_edge_m = fabsf(center_to_veh.length() - config.radius);
// Update depending on stage
if (!reached_edge) {
update_drive_to_radius();
} else if (dist_to_edge_m > 2 * MAX(g2.turn_radius, AR_CIRCLE_REACHED_EDGE_DIST) && !tracking_back) {
// if more than 2* turn_radius outside circle radius, slow vehicle by 20%
config.speed = 0.8 * config.speed;
GCS_SEND_TEXT(MAV_SEVERITY_WARNING, "Circle: cannot keep up, slowing to %.1fm/s", config.speed);
tracking_back = true;
} else if (dist_to_edge_m < MAX(g2.turn_radius, AR_CIRCLE_REACHED_EDGE_DIST) && tracking_back) {
// if within turn_radius, call the vehicle back on track
tracking_back = false;
} else {
update_circling();
}
g2.pos_control.update(rover.G_Dt);
// get desired speed and turn rate from pos_control
const float desired_speed = g2.pos_control.get_desired_speed();
const float desired_turn_rate = g2.pos_control.get_desired_turn_rate_rads();
// run steering and throttle controllers
calc_steering_from_turn_rate(desired_turn_rate);
calc_throttle(desired_speed, true);
}

